QPC Layer Architecture
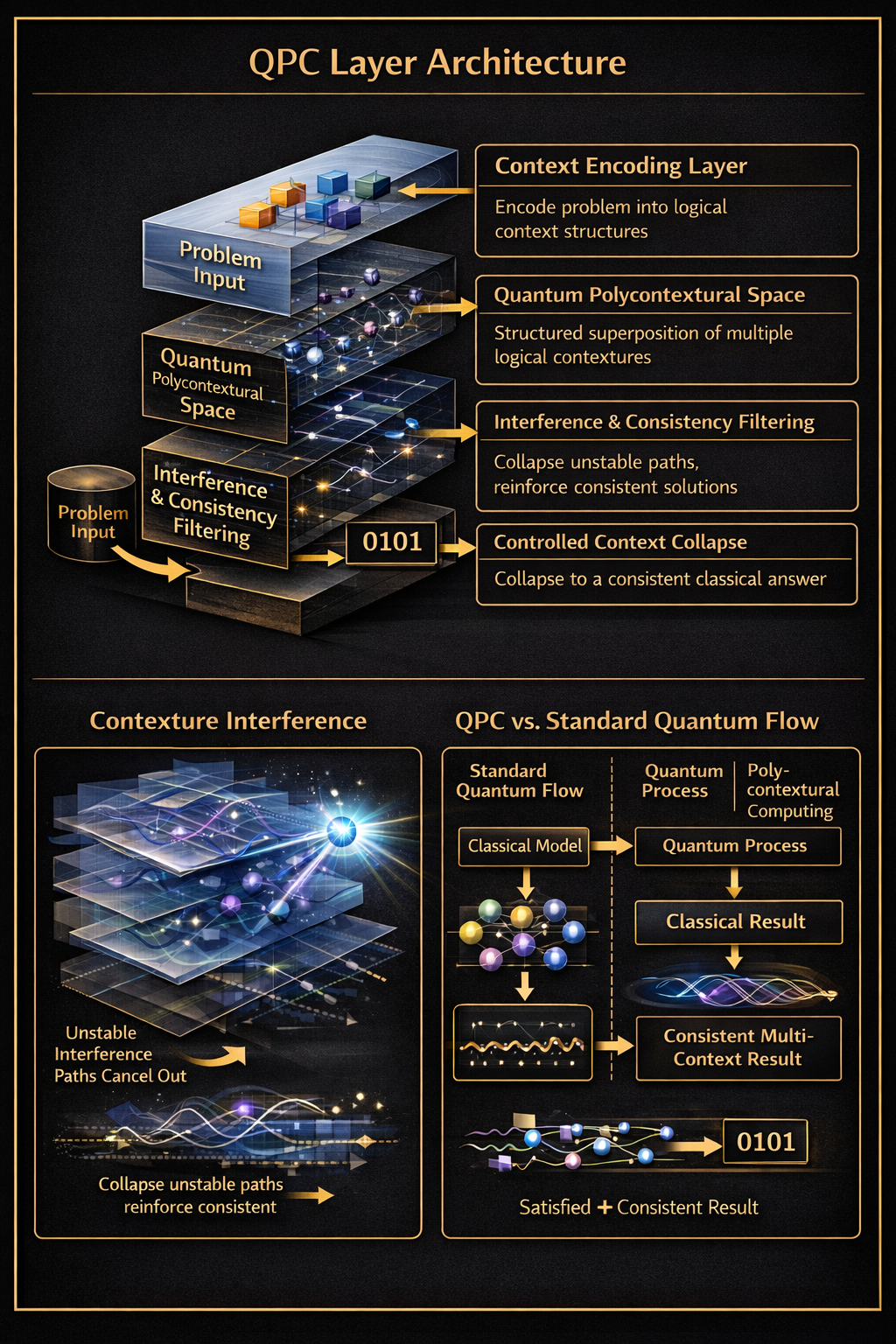
The image uses simplified presentation terms, while the codebase uses technical terms:
| Image Term | QPC Technical Term |
| Context Encoding | Kenogrammatic/Morphogrammatic encoding |
| Polycontextural Space | Multiple contextures with morphograms |
| Interference Filtering | Transjunctional operations + consistency |
| Context Collapse | Contextural collapse (measurement) |